Sneature - waste based footwear

Useful information
- Team members
- Emilie Burfeind
- Country
- Germany
- Keywords
- biodegradable sneaker sustainable fashion circular design environment centered design
Short Description
Sneature is the design of a waste-based, customisable and biodegradable sneaker.
Detailed Description
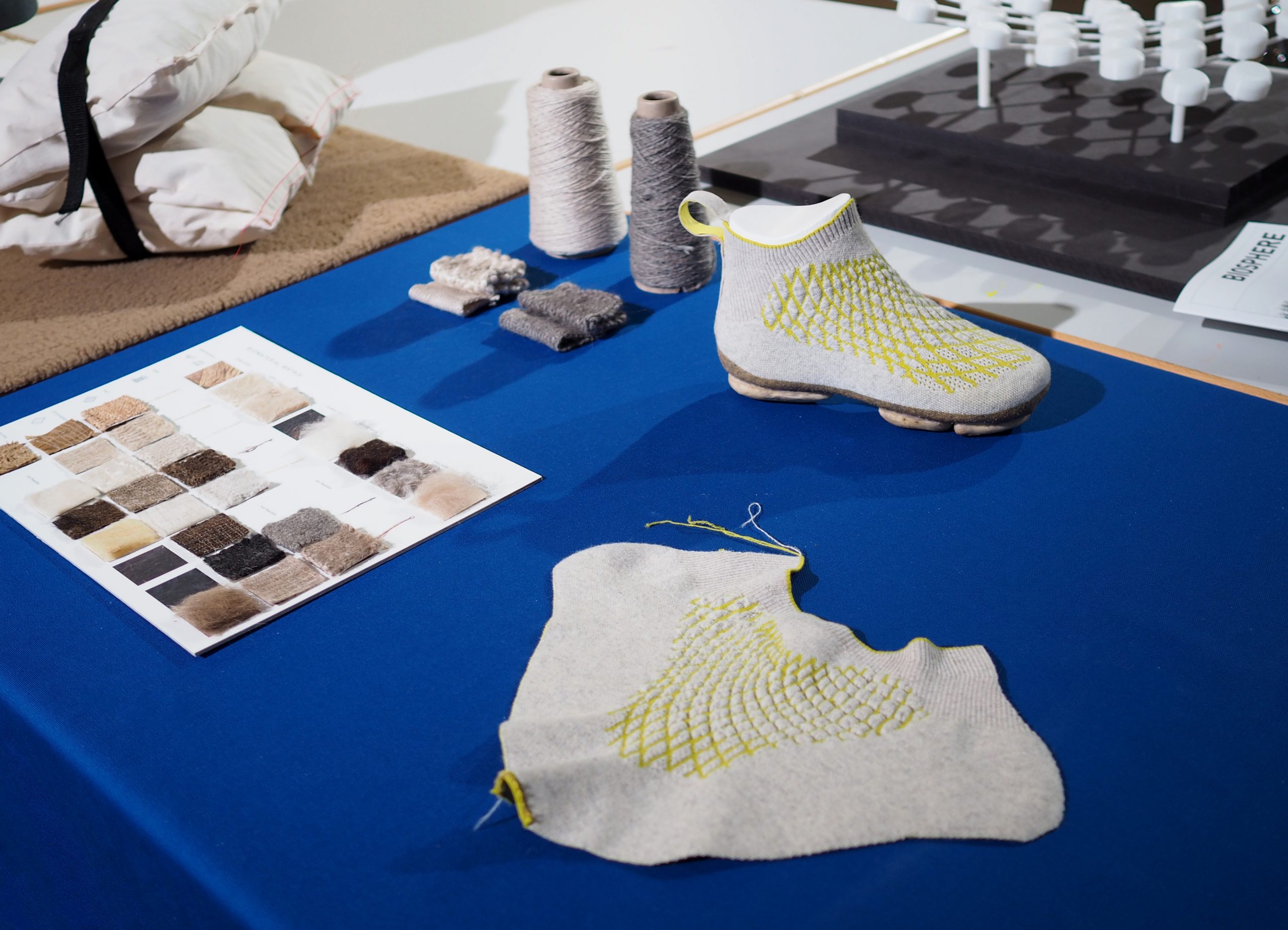
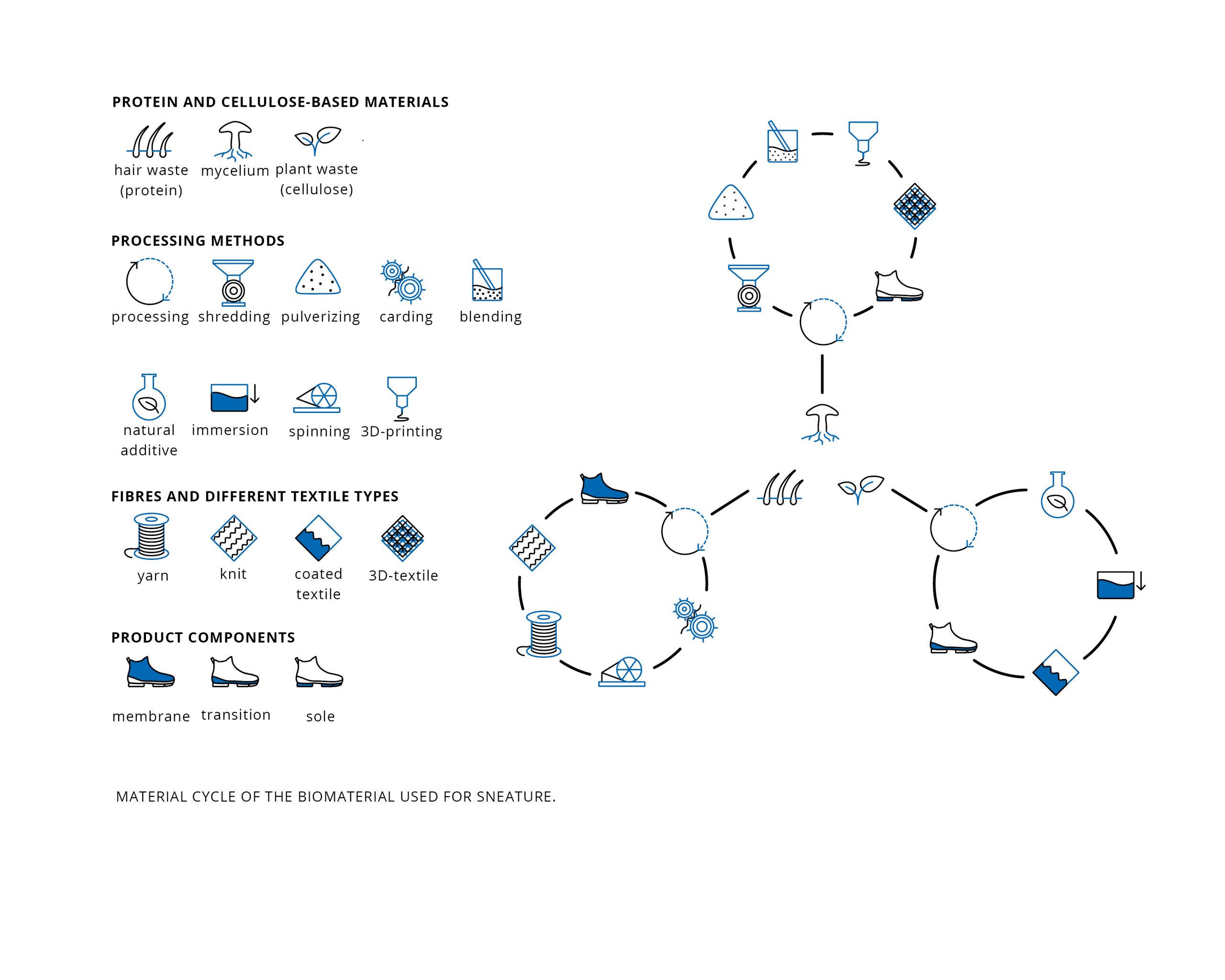
Sneature is the design of a waste-based sneaker. Upcycled waste- and raw materials were explored which led to the development of a biological material cycle for a sneaker. The use of additive manufacturing methods, such as 3D printing or 3D knitting, enable both individualization and on-demand production with the lowest possible energy consumption. In a microfactory, Sneature can be produced decentrally using local raw materials and involving the local community in production and strengthening it.
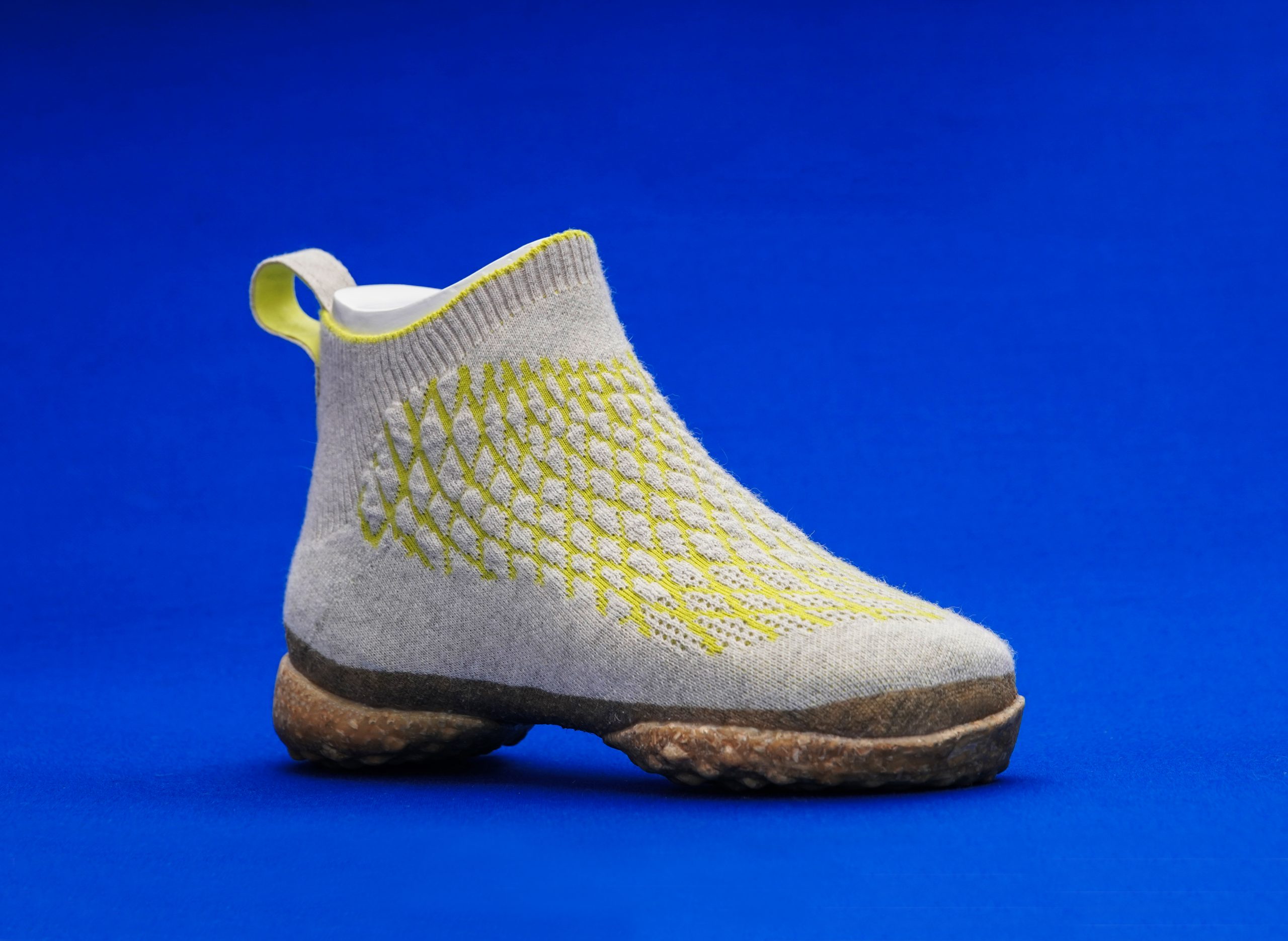
Reducing the product to its minimal components, it consists of a 3D-knitted membrane made of chiengora (yarn made from canine hair), a transitional area made of natural rubber, and a sole made of 3D-printed mushroom mycelium. After use, Sneature is biodegradable and can be returned as nutrients to the natural material cycle.
Project Details
- Does your design take social and cultural challenges and human wellbeing into consideration?
Sneature is the design of a framework which integrates the user into the design process through customisation possibilities. Furthermore, it is a concept that is manufactured locally in micro-factories. This means that, depending on specific conditions on site, regional raw materials can be used and local people can participate in the production process. This can make decentralised places more accessible and strengthen the local community.
- Does your design support sustainable production, embodying circular or regenerative design practices?
A large share of global emissions is caused by the clothing industry. Trainers are also among the clothing products that are often thrown away after a short life span. The complicated construction and the use of different materials (rubber, textiles, various plastics, etc.) make it almost impossible as well as unprofitable to disassemble and recycle a pair of trainers after use. Compared to conventional trainers, Sneature is reduced to minimal components and consists of only three parts: An upper, a transition area and a sole. In addition, the materials used in Sneature are biological raw and waste materials, such as dog hair, which is upcycled into industrially processable yarn, or mushroom mycelium, which is turned into a stable composite material with the help of plant waste materials. For each of the three raw materials used, a material cycle was developed that incorporates a low energy input in production. Here, not only are digital design methods used to adapt the product to the user, but also, in combination with additive manufacturing processes such as 3D printing or 3D knitting, the possibility of being able to produce even a small number of shoes locally in microfactories is demonstrated.
- Does your design promote awareness of responsible design and consumption?
The limited lifespan of the product reflects the current way textile products are handled. They are often worn little and after a short time disposed of in landfills or incinerated. This way of dealing with resources is only conditionally compatible with the self-renewal rate of our planet. This implies that the resources used in products should be used within "planetary boundaries".
Sneature as a sustainable alternative not only draws attention to our consumption behaviour of clothing, but also shows a solution approach. Because in the future, the question of the raw materials we can use for products will become more and more pressing. It is also becoming increasingly important to further explore the potential of waste materials from the food or agricultural industry. Responsible use of resources means investigating the potential of existing natural materials and integrating them into today's design and production processes.Innovative design options such as algorithm-based design make it possible to customise a shoe within defined framework conditions, which involves the user more in the design process. The use of small, high-tech manufacturing facilities ("microfactories") also enables sneakers to be produced decentrally. Sneature uses a holistic design concept to show the complexity of factors that are significant for an "ecological" product.
Images